Professional Stainless Steel Wire Mesh Manufacturer and Stockist from China.
Feel free to call or email our senior sales.
+61 435 598 786
+86 158 0318 7372
hello@metartmesh.com
+61 435 598 786
+86 158 0318 7372
hello@metartmesh.com
Hastelloy Wire Mesh and Wire Cloth
Material: C22 alloy wires and alloy C276 Wires
Type: Industrial Exotic Alloy Mesh
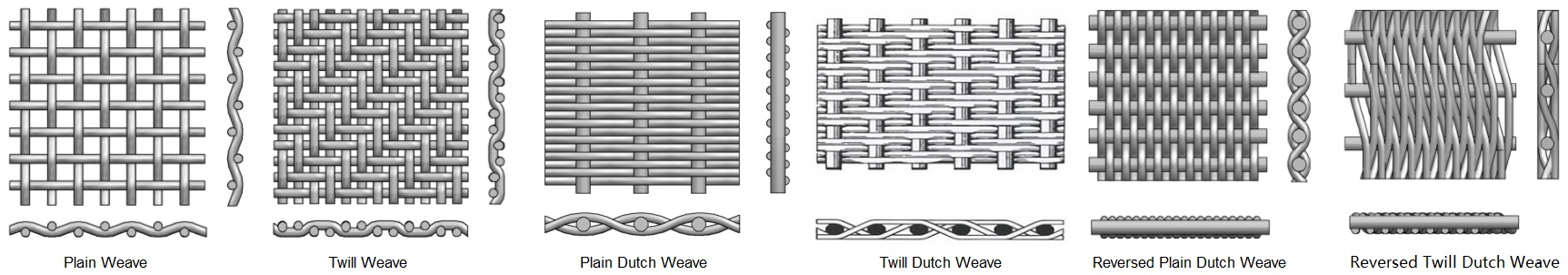
Weave Pattern: Plain and Twill Weave, Plain & Twill Dutch Weave, Crimped
Mesh Count: Customized.
Wire Diameter: Customized.
Roll Width: Customized.
Roll Length: Within 30M or other customized length.
METART mainly produces two types of Hastelloy wire mesh, including Hastelloy C22 and C276 mesh. These two grades of Hastelloy mesh are the most commonly used mesh for Hastelloy. If you are looking for other Hastelloy grades, please ask our sales team for availability or have a customized one.
#1,Hastelloy C-22 Wire Mesh
This alloy C22 mesh is well known by the public for its brand name Hastelloy® C-22 wire mesh. And it is also named as its UNS equivalent N06022 wire mesh and Werkstoff's #2.4602 wire mesh.
Alloy C22 is a nickel-molybdenum-chromium-tungsten super alloy that contains 56% of Nickel, 22% of Chromium, and 13% of Molybdenum element.
|
EQUIVALENT STANDARDS OF ALLOY C22 WIRE MESH |
||||
|
ALLOY C22 |
UNS |
ASTM |
EURONORMS EN |
JIS |
|
HASTELLOY C-22 |
N06022 Wire Mesh |
N06022 Wire Mesh |
EN 2.4602 Wire Mesh NiCr21Mo14W |
H 4551:2000 Wire Mesh |
Chemical Composition of Nickel Alloy C-22 wire mesh
|
Ni % |
Cr % |
Mo % |
Fe % |
W % |
Mn % |
Co % |
V % |
Si % |
C % |
S % |
P % |
|
56.0 Balance |
20.0-22.5 |
12.5-14.5 |
2.0-6.0 |
2.5-3.5 |
0.5Max |
2.5Max |
0.35Max |
.08Max |
0.01Max |
0.02Max |
0.02Max |
Physical Properties of Hastelloy C22 wire mesh
|
Physical Property |
°F |
British Units |
°C |
Metric Units |
|
Density |
75°F |
0.314 lb./in.(3) |
24°C |
8.69 g/cm(3) |
|
Melting Range |
2475-2550°F |
… |
1357-1399°C |
… |
|
Electrical |
75°F |
44.8 microhm-in. |
24°C |
1.14 microhm-m |
|
212°F |
48.3 microhm-in. |
100°C |
1.23 microhm-m |
|
|
392°F |
48.7 microhm-in. |
200°C |
1.24 microhm-m |
|
|
572°F |
49.3 microhm-in. |
300°C |
1.25 microhm-m |
|
|
752°F |
49.6 microhm-in. |
400°C |
1.26 microhm-m |
|
|
932°F |
49.9 microhm-in. |
500°C |
1.27 microhm-m |
|
|
1112°F |
50.2 microhm-in. |
600°C |
1.28 microhm-m |
|
|
Mean Coefficient |
75-200°F |
6.9 microin./in.-°F |
24-93°C |
12.4 X 10(-6)m/m-K |
|
75-400°F |
6.9 microin./in.-°F |
24-204°C |
12.4 X 10(-6)m/m-K |
|
|
75-600°F |
7.0 microin./in.-°F |
24-316°C |
12.6 X 10(-6)m/m-K |
|
|
75-800°F |
7.4 microin./in.-°F |
24-427°C |
13.3 X 10(-6)m/m-K |
|
|
75-1000°F |
7.7 microin./in.-°F |
24-538°C |
13.9 X 10(-6)m/m-K |
|
|
75-1200°F |
8.1 microin./in.-°F |
24-649°C |
14.6 X 10(-6)m/m-K |
|
|
75-1400°F |
8.5 microin./in.-°F |
24-760°C |
15.3 X 10(-6)m/m-K |
|
|
75-1600°F |
8.8 microin./in.-°F |
24-871°C |
15.8 X 10(-6)m/m-K |
|
|
75-1800°F |
9.0 microin./in.-°F |
24-982°C |
16.2 X 10(-6)m/m-K |
|
|
Thermal |
118°F |
70 Btu-in/ft²-hr-°F |
48°C |
10.1 W/m-K |
|
212°F |
77 Btu-in/ft²-hr-°F |
100°C |
11.1 W/m-K |
|
|
392°F |
93 Btu-in/ft²-hr-°F |
200°C |
13.4 W/m-K |
|
|
572°F |
108 Btu-in/ft²-hr-°F |
300°C |
15.5 W/m-K |
|
|
752°F |
121 Btu-in/ft²-hr-°F |
400°C |
17.5 W/m-K |
|
|
932°F |
135 Btu-in/ft²-hr-°F |
500°C |
19.5 W/m-K |
|
|
1112°F |
148 Btu-in/ft²-hr-°F |
600°C |
21.3 W/m-K |
|
|
Thermal |
70°F |
0.004 in²/sec |
21°C |
2.7 x 10(-6)m²/s |
|
212°F |
0.005 in²/sec |
100°C |
3.0 x 10(-6)m²/s |
|
|
392°F |
0.005 in²/sec |
200°C |
3.5 x 10(-6)m²/s |
|
|
572°F |
0.006 in²/sec |
300°C |
3.9 x 10(-6)m²/s |
|
|
752°F |
0.007 in²/sec |
400°C |
4.2 x 10(-6)m²/s |
|
|
932°F |
0.007 in²/sec |
500°C |
4.6 x 10(-6)m²/s |
|
|
1112°F |
0.007 in²/sec |
600°C |
4.8 x 10(-6)m²/s |
#2, Hastelloy C-276 Wire Mesh
With the brand name Hastelloy® C-276, Alloy C 276 wire mesh is the by far the most widely used alloy in the Hastelloy family. It is also known by the public as UNS N10276 wire mesh and number 2.4819 wire mesh which is a nickel-molybdenum-chromium alloy, with the addition of tungsten and extremely low content of carbon and silicon which will minimize carbide precipitation during welding to maintain corrosion resistance in as-welded structures. Hastelloy C276 wire mesh performs excellent resistance in a wide variety of chemical process environments including those with ferric and cupric chlorides, hot contaminated organic and inorganic media, chlorine, formic and acetic acids, acetic anhydride, seawater, brine and hypochlorite, and chlorine dioxide solutions.
Similarities and differences between C22 and C276
Both Alloy C22 and C276 are very important alloys in the family of Hastelloy super alloys. But C22 wire mesh and C276 wire mesh have different applications in the chemical industry due to their different chemical compositions.
The major difference between Alloy C22 and C276 is that the Hastelloy C22 is very important due to its enhanced versatility and excellent resistance to chloride-induced pitting whereas the Hastelloy C276 is very important due to its proven performance in a wide range of aggressive chemicals.
Alloy C-22 wire mesh is a great alternative when super austenitic stainless steel wire mesh such as AL-6XN® wire mesh, 904L wire mesh, and duplex stainless steels (2205 wire mesh and 2507 wire mesh) will not withstand extremely aggressive media. This is because it is a nickel-chromium-molybdenum-tungsten alloy wire mesh with better overall resistance to uniform and localized corrosion than any other Ni-Cr-Mo alloy wire mesh.
Alloy C-22 wire mesh and C276 wire mesh have many similarities which always leads to confusion. But alloy C22 wire meshes are proven to have a better overall corrosion resistance compared to C-276 mesh and are often referred to as the upgrade version of C-276 mesh products.
Hastelloy C-22 wire mesh should not be used in service temperatures above 1250°F (676℃) due to the formation of detrimental phases which form above this temperature.
The density of C22 wire mesh is 8.7g/cm3 whereas the C276 alloy is 8.9g/cm3. But C22 is generally a bit more expensive as the manufacturing cost of C22 alloy is higher than that of Hastelloy C276. In most cases, these 2 different Hastelloy grades can be replaced with each other. But C276 mesh products are more versatile and alloy C22 products perform a bit better in applications.
©COPYRIGHT METART BUILDING TEC CO., LTD | ALL RIGHTS RESERVED | PRIVACY POLICY